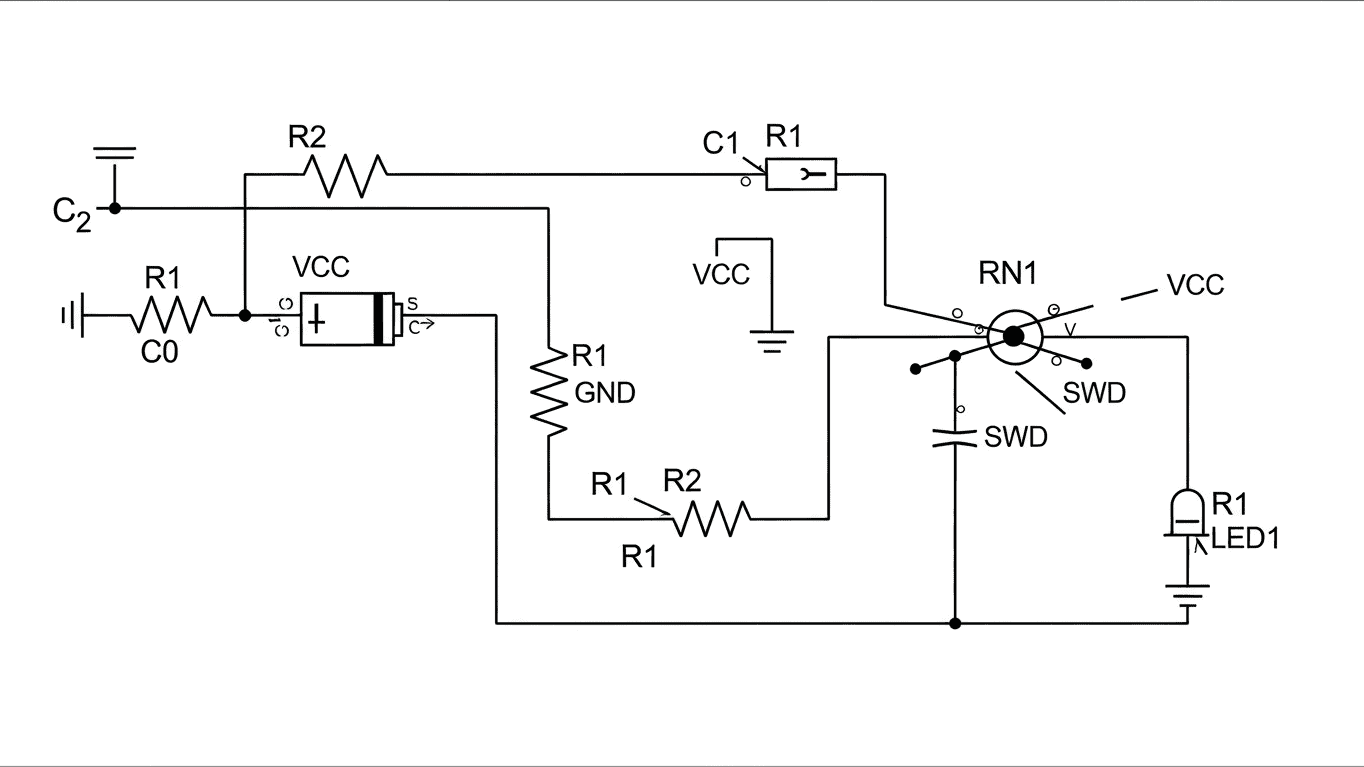
Understanding the "Traveller Wireless Remote Control Wiring Diagram" is essential for anyone looking to install or troubleshoot a wireless remote control system for their traveller setup. This diagram acts as a blueprint, outlining the connections between the receiver unit, the power source, and the actual devices being controlled. Whether you're looking to automate your campsite, boat, or any other mobile application, a clear grasp of this wiring diagram ensures safe and efficient operation.
Demystifying the Traveller Wireless Remote Control Wiring Diagram
At its core, a "Traveller Wireless Remote Control Wiring Diagram" illustrates the electrical pathways for a wireless remote system designed for mobile or portable use. It details where each wire should connect to ensure the remote transmitter can send signals to the receiver, which in turn activates or deactivates the connected devices. This diagram is crucial for several reasons:
- Safety: Incorrect wiring can lead to short circuits, damage to equipment, or even fire hazards. The diagram ensures proper grounding and connection of power, minimizing risks.
- Functionality: It guarantees that all components communicate effectively. Without the correct connections, your remote will simply not work.
- Troubleshooting: When issues arise, the wiring diagram is your primary tool for diagnosing problems, allowing you to pinpoint faulty connections or components.
The typical setup involves a few key components, all represented in the "Traveller Wireless Remote Control Wiring Diagram":
- The Transmitter: This is the handheld remote you operate. It sends a radio frequency signal.
- The Receiver: This unit is usually mounted near the devices being controlled. It picks up the signal from the transmitter.
- The Controlled Devices: These are the items you want to operate wirelessly, such as lights, winches, or pumps.
- The Power Source: This provides the necessary electricity for both the receiver and the controlled devices.
A simplified representation of these connections might look something like this:
| Component | Connection Point | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Transmitter | N/A (Transmits wirelessly) | Initiates commands |
| Receiver | Power Input (from Power Source) | Receives power to operate |
| Receiver | Control Output (to Controlled Devices) | Sends signals to activate/deactivate devices |
| Power Source | Connected to Receiver and Controlled Devices | Supplies electricity |
The "Traveller Wireless Remote Control Wiring Diagram" often includes details about wire gauges, connector types, and even specific pin assignments. For instance, you might see designations like "+12V" for positive power, "GND" for ground, and specific output terminals labeled "Output 1," "Output 2," etc., corresponding to different functions or devices. Following this diagram precisely is paramount for a successful and reliable installation.
If you're ready to get your hands on the specific "Traveller Wireless Remote Control Wiring Diagram" for your particular system, please refer to the comprehensive guide provided by the manufacturer or the technical documentation accompanying your equipment.